poisson ratio tensile test|poisson's ratio formula : trader Poisson's ratio is a measure of the Poisson effect, the phenomenon in which a material tends to expand in directions perpendicular to the direction of compression. Conversely, if the material is stretched rather than compressed, it usually tends to contract in the directions transverse to the direction of stretching. It is a common observation when a rubber band is stretched, it becomes noticeably thinner. Again, the Poisson ratio will be the ratio of relative contraction to relative exp. MG1, MG2, Bom Dia Minas e g1 Minas. 43.181 curtidas · 329 falando sobre isso. Telejornal que traz as notíciais locais, mostrando o que acontece na sua.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Apple TV. PTV Sports Official Transmission. PTV Sports provides its users with the latest Pakistan & International Sports news including Cricket, Football, Hockey, Tennis, Squash, Boxing & Snooker. Watch Live transmission of ICC Cricket World T20 and other sports events, .
Poisson’s Ratio (𝜈) = transverse strain / axial strain. 𝜈 = - 𝜀 l a t e r a l 𝜀 a x i a l. Where: 𝜈 is the Poisson’s ratio. ε lateral is the lateral strain (strain in the direction perpendicular to the direction of force) ε axial is the axial strain (strain along .Poisson's ratio is a measure of the Poisson effect, the phenomenon in which a material tends to expand in directions perpendicular to the direction of compression. Conversely, if the material is stretched rather than compressed, it usually tends to contract in the directions transverse to the direction of stretching. It is a common observation when a rubber band is stretched, it becomes noticeably thinner. Again, the Poisson ratio will be the ratio of relative contraction to relative exp. In this article, we will present a step-by-step guide on calculating Poisson’s ratio from tensile test data using a Poisson ratio calculator. Background. Poisson’s ratio is defined .ASTM D638, Appendix A3 provides guidance for measuring the Poisson ratio of plastics in tension and suggests the use of a Type I tensile specimen and a testing speed of 5 mm/min.
Poisson’s ratio is a mechanical property often used in Finite Element Analysis (FEA) calculations to predict the stresses a product may see in an end use application. It should be calculated from the initial portion of the .Poisson’s Ratio is a measure of transverse strain against axial strain when uniaxial stress is applied. Test Procedure: The specimen is clamped into the grips of the Instron universal .Poisson's ratio is the ratio of expansion along one axis to contraction along the opposite axis when a material is subjected to tensile or compressive forces. Applying tensile strain to a rubber band, for example, causes it to elongate . Tension test, alternatively referred to as tensile testing or uniaxial tension test, is one of the most commonly used tests to determine important material parameters such as Young’s modulus, yield strength, ultimate .
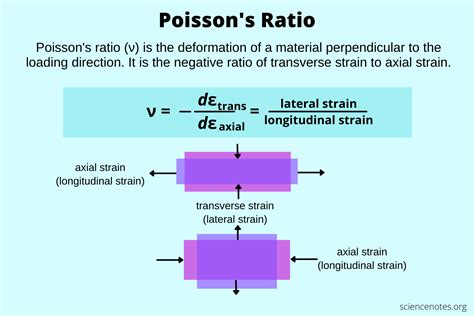
If volume is conserved, the Poisson’s ratio is 0.5 (see proof here). Since the strain is small for most of the elastic deformation, it is a good approximation to assume volume change is negligible. Poisson’s ratio (symbol ν or nu) or is a mechanical property of a material that is the measure of its deformation perpendicular to the direction of loading. In other words, it is the negative value of the ratio of transverse or . where: v v v — Poisson's ratio (dimensionless);; ε trans \varepsilon_\text{trans} ε trans — Transverse (lateral) strain - the relative change in the dimension perpendicular to the direction of force; and; ε axial . Yes, you can use a tensile test with a circular cross section to calculate the Poisson ratio µ. Poisson's ratio is defined as the negative of the ratio of the lateral strain to the axial strain .
Poisson's ratio is not expressed in units and is generally positive, because all common materials experience narrowing in their cross-sectional area during tensile testing. Most materials have a Poisson’s ratio between 0 and 0.5, .ASTM D638, Appendix A3 provides guidance for measuring the Poisson ratio of plastics in tension and suggests the use of a Type I tensile specimen and a testing speed of 5 mm/min. The researcher should take care to report all details of the experimental method as well as the bounds for determining the linear elastic region in which the Poisson .
Tensile Young’s modulus, Poisson’s ratio and tensile strength can be accurately estimated from one single Brazilian tensile test. The specific conclusions from this work include: 1. The analytic solutions of tensile elastic modulus and Poisson’s ratio for Brazilian disc were derived based on stress distribution of isotropic materials. 2. However, when performing a test on a material with a known Poisson’s ratio, we were receiving a value of about 25 percent lower than it should have been. After recalibrating the extensometers and careful review of our process, we came to the realization that the spring pressure in the transverse extensometer was set too high and was digging .Static Measurement of Poisson’s Ratio for Timber. Measurement of the Poisson’s ratio by the axial tension test. First, three pieces of lumber with nominal sizes of 300 mm × 40 mm × 12.2 mm that were sawn from a large board of Sitka Spruce with a width of 107 mm were taken as specimens in the dynamic test (the same specimen numbers were .The model shows how to estimate the Young's modulus and Poisson ratio based on a tensile test. The test measures the tensile force and the radial displacement for different values of the prescribed displacement. The model is based on synthetic data generated in the model itself. It is considered good practice to test parameter estimation models .
Since Poisson's ratio is a ratio of two strains, and strain is dimensionless, Poisson's ratio is also unitless. Poisson's ratio is a material property. Poisson's ratio can range from a value of -1 to 0.5. For most engineering materials, for example steel or aluminum have a Poisson's ratio around 0.3, and rubbers have a Poisson's ratio around 0. .For tensile deformation, Poisson’s ratio is positive. For compressive deformation, it is negative. Here, the negative Poisson ratio suggests that the material will exhibit a positive strain in the transverse direction, even though the longitudinal strain is positive as well. . Test your Knowledge on Poissons Ratio. Q 5. Put your . Learn about Poisson's Ratio in this article, its unit, symbol, and values for different materials along with its relation to Young's modulus, examples. . CUET English, Hindi & General Test 2024 Mock Test . 220 Total Tests | 7 Free Tests. . When a metallic rod of length 3 m and diameter 1 cm is subjected to a tension of 800 N, the diameter .
The indirect tensile test was carried out on five types of asphalt mixtures to analyze the effect of different asphalt and different mix grading types on Poisson's ratio, and the recommended .Tensile Testing is a destructive engineering and materials science test whereby controlled tension is applied to a sample either as a load for proof testing or until it fully fails. . strain hardening characteristics, Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio. If you have any questions or need help, email us to get expert advice: [email protected] . elastic, room-temperature tensile, room-temperature high strain rate, impact, and elevated-temperature tensile. Specimens of 29 different steels representing the 12 identified strength levels in the building as built were characterized. Elastic properties include modulus, E, and Poisson’s ratio, ν, for temperatures up to 900 °C.
Tensile testing of composites is generally in the form of basic tension or flat-sandwich tension testing in accordance with standards such as ISO 527-4, ISO 527-5, ASTM D 638, . Stress is calculated by the ratio of applied load P to the cross-sectional area (A). The changes in length and area are recorded simultaneously and are used as inputs .The Poisson's ratio of Sylgard 184 was found to be . FEM simulations and numerical mathematics to determine the Poisson's ratio, without any additional tensile testing setup or advanced tracking methods, in particular since . Poisson's ratio is the ratio of the relative contraction strain (that is, the . How to Convert a Load to PSI in a Tensile Test . How to Calculate Young's Modulus . How to Size H-Beams . How to Calculate Maximum Stress .Definition of Poisson's ratio Poisson's ratio is the ratio of transverse contraction strain to longitudinal extension strain in the direction of stretching force. Tensile deformation is considered positive and compressive deformation is considered negative. The definition of Poisson's ratio contains a minus sign so that normal materials have a positive ratio.
vonroc pro vochtmeter
With Poisson's ratio for aluminum 0.334 - the contraction can be calculated as. dr = - 0.334 ( 100 10-3 m ) ( 5 10-3 m) / (10 m) = 1.7 10 -5 m = 0.017 mm . Poisson's Ratios for Common Materials. For most common materials the Poisson's ratio is in the range 0 - 0.5 . Typical Poisson's Ratios for some common materials are indicated below. In addition to the indirect tensile test (IDT) protocol to determine the dynamic modulus and Poisson’s ratio [17], Di Benedetto et al. [9] conducted tension–compression cyclic tests to evaluate the dynamic modulus and Poisson’s ratio simultaneously. For isotropic materials such as asphalt mixtures, Poisson’s ratio should be between 0.1 and 0.5 in the linear elastic range under normal conditions [6], [7].However, the specific range of variation of Poisson's ratio in indirect tensile measurements of asphalt mixtures has not been well understood in past studies.
Test ID. M-101. Description. A universal testing machine (UTM) is used to determine and report the Poisson's ratio (the ratio of transverse strain to axial strain resulting from uniform axial stress below the elastic limit of the material). Tensile Modulus (test ) is also reported. The sample is loaded between the grips of the UTM.Scope of ASTM D638 Test Method: ASTM D638 and ISO 527 are technically equivalent test methods. Poisson’s Ratio is a measure of transverse strain against axial strain when uniaxial stress is applied. The uniaxial force is used to deform the sample in both axial and lateral directions. A high tensile modulus means that the test [.]
where ε x and ε z are the elastic strains in the lateral and longitudinal directions at the same tensile stress. The Poisson’s ratio for most metals is about 0.3 and for carbon fibre–epoxy composites is typically 0.2–0.3. Poisson’s ratio is an important engineering property for aerospace materials because of the need for close tolerances in aircraft structures and engines. What Poisson’s Ratio Means. Most materials have Poisson’s ratio values ranging between 0.0 and 0.5. Soft materials, like rubber, have Poisson’s ratio values near 0.5. Steel and rigid polymers typically have values around 0.3. Porous materials typically have Poisson’s ratio values close to zero. This is because they collapse when . Abstract. Increased interest in mechanistic evaluation of flexible pavement structures has brought a demand for accurate and practical methods, models, or both to estimate the mechanical properties of asphalt concrete mixtures. One of these properties is the Poisson’s ratio (ν) of asphalt concrete mixtures, which is often assumed to have a constant value of 0.35 .The Poisson’s ratio of nacre became a negative value and was computed to be about 0:38, which is a novel value of Poisson’s ratio that has not been found in existing materi-als, and when the longitudinal strain was greater than 9:2 10 3 and up to the failure of the sample, the transverse strain remained a constant and the Poisson’s ratio .
what is poisson's ratio
strain ratio of poisson
poisson's ratio temperature
WEB5 de mar. de 2021 · The savage dogs tore all of the skin off of Pereira's face before he was rescued by brave passersby Credit: Unomidias. Pereira was enjoying his regular .
poisson ratio tensile test|poisson's ratio formula